Sequence and Safety Planning for Critical Lifts
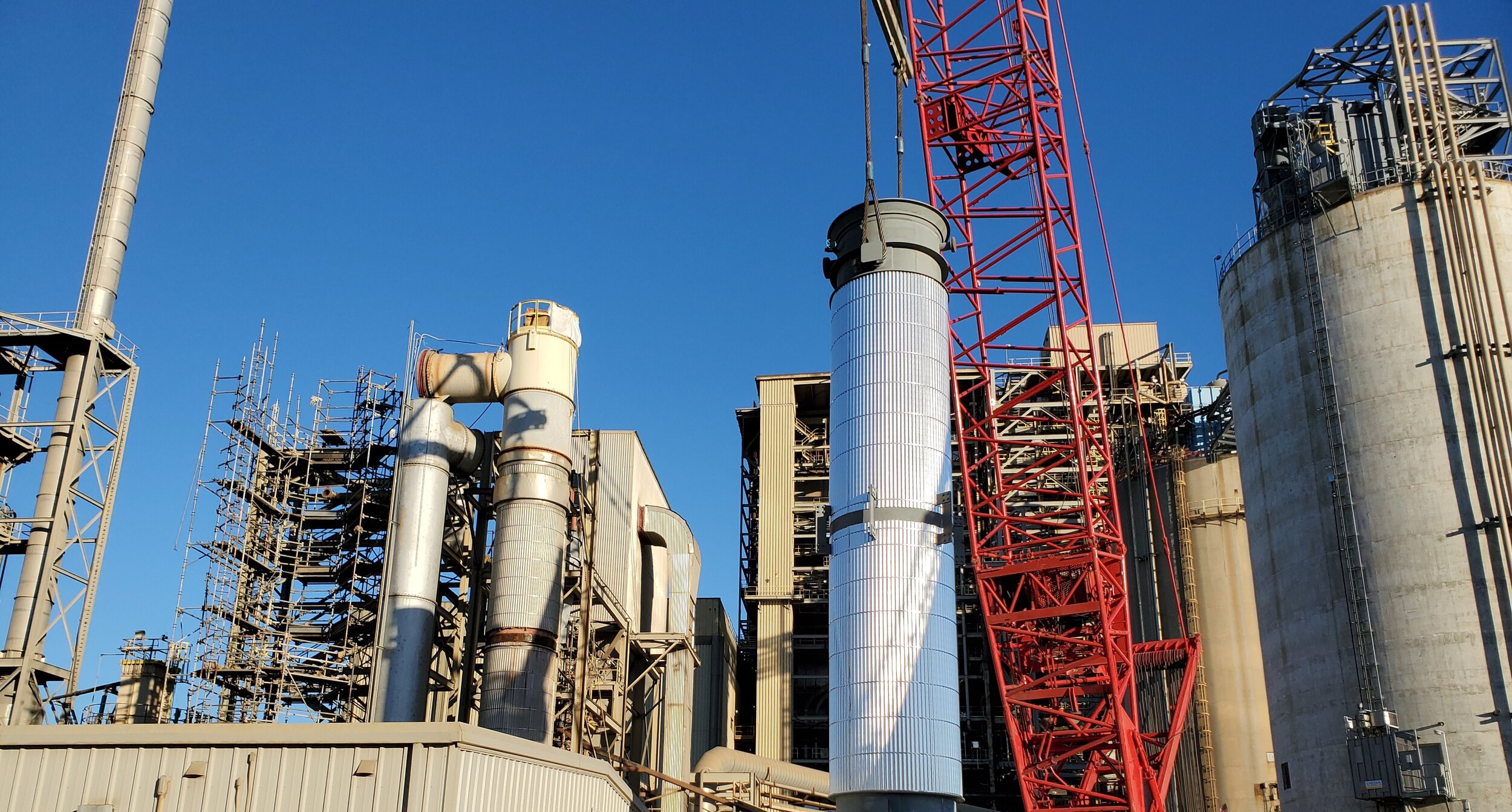
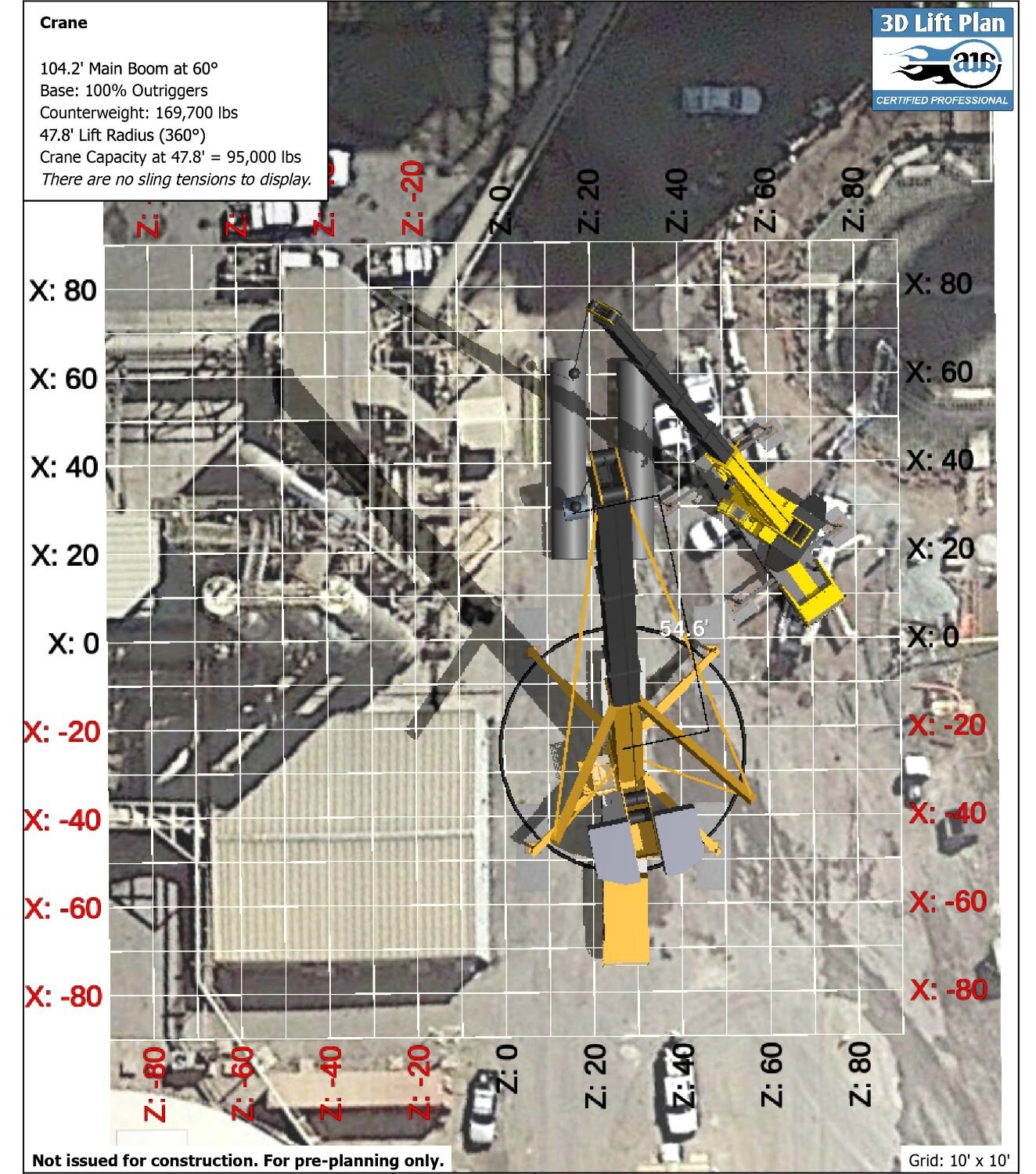

A critical lift is defined by OSHA as a lift that exceeds 75% of the rated capacity of the crane or requires the use of more than one crane. At SEFA, we recognize that there are number of conditions that can make a lift “critical,” such as tight site constraints, people working in lifts next to a suspended load, or awkward loads that might shift during rigging. Lift plans include necessary details for the crane operation sequence and a plan for job safety.
Contractors begin the planning effort by working with a crane company to develop a lift plan. Software-generated lift plans rely on information such as equipment weight, equipment dimensions, and site conditions to create a scaled drawing of the project site including proposed crane locations, lift area, boom length and angles, and locations of equipment being lifted.
Once the lift plan is reviewed and approved, the project manager outlines where equipment will be staged on the ground so that it will end up in the correct position in the air. For equipment replacement projects, this includes detailing the loading, unloading, and transportation sequence since new and old equipment might be transported and staged some distance away.
Included in the lift planning process is a Job Safety Analysis to create a plan for safety. Lift safety plans can include the following tasks:
Plan and host a pre-lift meeting to review safety procedures and lift plan sequence.
Designate a Competent Person to oversee the lift.
Verify that crane operator and rigger certifications are current.
Document inspections of the crane and all rigging prior to use, and make sure the crane model matches the one proposed on the lift plan.
Place barricades around the swing radius of the crane to prevent injury to personnel.
Verify outrigger placement and the use of load distribution mats, and confirm that the terrain is suitable to support the crane and the load.
Clear and secure the perimeter.
Assign a spotter for the operator and stage lookouts on the perimeter to prevent personnel from entering the area during the lift.
Use tag lines to assist in controlling the load while keeping personnel away from the load.
